 My Own, My Native Land
My Own, My Native Land
Entry Category: Literature and Authors
 My Own, My Native Land
My Own, My Native Land
 The Mysterious Benedict Society
The Mysterious Benedict Society
Newberry, Farrar Claudius
Newth, Rebecca
aka: Rebecca Newth Harrison
Noland, Fent
aka: Charles Fenton Mercer (Fent) Noland
 Fent Noland Grave
Fent Noland Grave
Northwest Arkansas Writers
 Notorious
Notorious
 M. E. Oliver's Strange Scenes in the Ozarks
M. E. Oliver's Strange Scenes in the Ozarks
 On a Slow Train Through Arkansaw
On a Slow Train Through Arkansaw
On a Slow Train Through Arkansaw
One With Others
 One With Others
One With Others
Oxford American (OA)
Ozark Trilogy, The
 Ozarks Double Homicide
Ozarks Double Homicide
 Ozarks Missing Person
Ozarks Missing Person
 Ozarks Witness Protection
Ozarks Witness Protection
 Painted House Museum
Painted House Museum
Painted House, A
Palmer, Bob
aka: Robert Franklin Palmer Jr.
 Ted Parkhurst
Ted Parkhurst
 Ted Parkhurst of August House
Ted Parkhurst of August House
Pendleton, Donald Eugene (Don)
Peter, Lily
Pettigrew, Helen Lyle
Pharr, Suzanne
 Suzanne Pharr
Suzanne Pharr
Philip Hall Likes Me, I Reckon Maybe
 Philological Review
Philological Review
Piazza, Ben Daniel
Pickens, William
 William Pickens
William Pickens
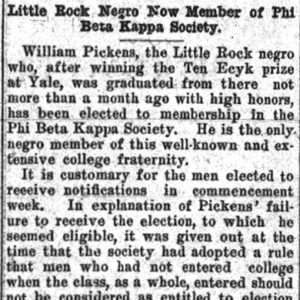 William Pickens Article
William Pickens Article
Pike, Albert
Plum Thicket, The
 The Plum Thicket
The Plum Thicket
Poesia
Poets Laureate of Arkansas
Poets’ Roundtable of Arkansas (PRA)
Porter Prize
aka: Porter Fund Literary Prize
Portis, Charles McColl
Powell, Nate
Primary Colors
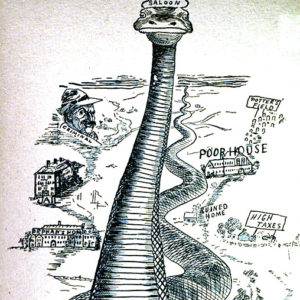 Pro-temperance Cartoon
Pro-temperance Cartoon
Promise Me Always
 Promise Me Always
Promise Me Always
 Promises from the Past
Promises from the Past
 A Pryor Commitment
A Pryor Commitment




