Entry Category: Attractions (Historic and Current)
 Corn Hole Spring
Corn Hole Spring
Crescent Hotel
 Crescent Hotel
Crescent Hotel
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center Walkway
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center Walkway
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center
 Crowley's Ridge Nature Center Entrance
Crowley's Ridge Nature Center Entrance
Crowley’s Ridge Parkway, National Scenic Byway
 Crystal River Tourist Court
Crystal River Tourist Court
 Daisy Airgun Museum Brochure
Daisy Airgun Museum Brochure
 De Soto Sculpture
De Soto Sculpture
 Delta Rivers Nature Center Boardwalk
Delta Rivers Nature Center Boardwalk
 Delta Rivers Nature Center Entrance
Delta Rivers Nature Center Entrance
 Delta Rivers Nature Center Side View
Delta Rivers Nature Center Side View
Diamond Cave
 Diamond Cave Postcard
Diamond Cave Postcard
 Dogpatch Characters
Dogpatch Characters
Dogpatch USA
 Dogpatch USA Performers
Dogpatch USA Performers
Elna M. Smith Foundation
aka: Five Sacred Projects
aka: Sacred Projects
 Ernie's Museum of Black Arkansas
Ernie's Museum of Black Arkansas
Esse Purse Museum
 Esse Purse Museum
Esse Purse Museum
 Esse Purse Museum Display
Esse Purse Museum Display
 Esse Purse Museum Display
Esse Purse Museum Display
 Farm Implement Display
Farm Implement Display
 First Free Bathhouse
First Free Bathhouse
 Forester Reunion Park
Forester Reunion Park
 Forester Reunion Park
Forester Reunion Park
Forrest L. Wood Crowley’s Ridge Nature Center
 Free Bathhouse Construction
Free Bathhouse Construction
Front Porch Stage
 Front Porch Stage Audience
Front Porch Stage Audience
 Front Porch Stage
Front Porch Stage
Garvan Woodland Gardens
 Garvan Woodland Gardens Bridge
Garvan Woodland Gardens Bridge
 Garvan Woodland Gardens Waterfall
Garvan Woodland Gardens Waterfall
 Garvan Woodland Gardens
Garvan Woodland Gardens
 Government Free Bathhouse
Government Free Bathhouse
Governor Mike Huckabee Delta Rivers Nature Center
aka: Delta Rivers Nature Center
Great Passion Play
aka: Passion Play
 Great Passion Play
Great Passion Play
 Great Passion Play
Great Passion Play
 Great River Road Sign
Great River Road Sign
Great River Road-Arkansas National Scenic Byway
 Great River Road Welcome Center
Great River Road Welcome Center
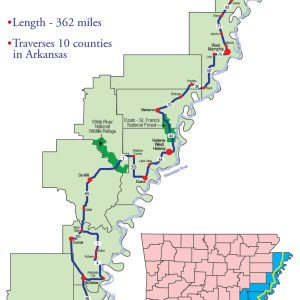 Great River Road Map
Great River Road Map




