 Napoleon and Mary Ann Buford
Napoleon and Mary Ann Buford
County: Phillips
 Napoleon and Mary Ann Buford
Napoleon and Mary Ann Buford
 Cadet Pilot
Cadet Pilot
Carter, Nathan (Execution of)
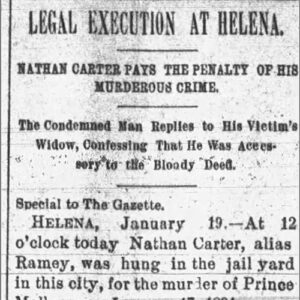 Nathan Carter Execution Article
Nathan Carter Execution Article
 Carvill Store
Carvill Store
 Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
 Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
 Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
 Centennial Baptist Church Repairs
Centennial Baptist Church Repairs
 Cherry Street
Cherry Street
 Cherry Street
Cherry Street
Cherry Street Historic District
 Cherry Street Historic District
Cherry Street Historic District
 Cherry Street Historic District
Cherry Street Historic District
 Chicago Mill and Lumber Company
Chicago Mill and Lumber Company
 Alida Clawson Clark
Alida Clawson Clark
Clark, Alida Clawson
Clark, Calvin
 Calvin Clark
Calvin Clark
Clark, Moses Aaron
 Georgia Clark
Georgia Clark
 M. A. Clark
M. A. Clark
Clarke, James Paul
 Patrick Cleburne
Patrick Cleburne
 Patrick Cleburne
Patrick Cleburne
 Patrick Cleburne Gravesite
Patrick Cleburne Gravesite
Cleburne, Patrick Ronayne
 Patrick Cleburne Statue
Patrick Cleburne Statue
Coleman, Ed “Sweat”
Coolidge House
 Coolidge House
Coolidge House
 Coolidge House
Coolidge House
Curtis, Samuel Ryan
 Cypress Logging
Cypress Logging
Davis, Ellis CeDell
 De Soto Monument
De Soto Monument
Delta Cultural Center
 Delta Cultural Center
Delta Cultural Center
 Delta Cultural Center
Delta Cultural Center
 Delta Cultural Center
Delta Cultural Center
 Delta Dirt Distillery
Delta Dirt Distillery
 Delta Heritage Trail
Delta Heritage Trail
 Delta Heritage Trail State Park
Delta Heritage Trail State Park
Delta Heritage Trail State Park
 Dixie Drive-in
Dixie Drive-in
Dobbins, Archibald
Dorsey, Stephen Wallace
 Doughboy Monument, Helena-West Helena
Doughboy Monument, Helena-West Helena
 Doughboy Monument, Helena-West Helena
Doughboy Monument, Helena-West Helena




