 Earle Baptist Church
Earle Baptist Church
County: Crittenden
 Earle Baptist Church
Earle Baptist Church
 Earle Church
Earle Church
 Earle Depot
Earle Depot
 Earle Flood
Earle Flood
 Earle High School
Earle High School
 Earle High School
Earle High School
 Earle Methodist Church
Earle Methodist Church
Earle Race Riot of 1970
 Earle Street Scene
Earle Street Scene
 Earle Street Scene
Earle Street Scene
 Earle Street Scene
Earle Street Scene
Earle, Josiah Francis
Edmondson (Crittenden County)
Edmondson Home and Improvement Company v. Harold E. Weaver
 Elaine Massacre Headlines
Elaine Massacre Headlines
Eskridge, Thomas P.
Eudy, Sid
aka: Sid Vicious
 Fleming Home
Fleming Home
 Fogleman Gin
Fogleman Gin
Fogleman, John Albert
Ford, L. L. (Execution of)
Fox, Warren (Lynching of)
 Warren Fox Lynching Article
Warren Fox Lynching Article
Gammon, John, Jr.
Garland, Mamie Odessa Hale
Gathings, Ezekiel Candler “Took”
George Berry Washington Memorial
Gilbert, John (Lynching of)
 John Gilbert Lynching Story
John Gilbert Lynching Story
Gilmore (Crittenden County)
Great Balls of Fire!
Green, Steve
Greenock (Crittenden County)
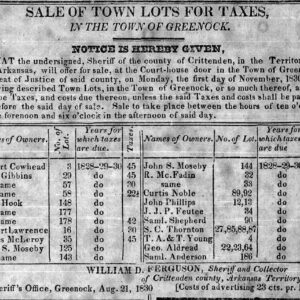 Greenock Land for Sale
Greenock Land for Sale
Greer, William Ezra
 Ezra and Jackie Greer
Ezra and Jackie Greer
 Greyhound Racing
Greyhound Racing
 Mamie Hale
Mamie Hale
Hallelujah
 Hauling Cotton
Hauling Cotton
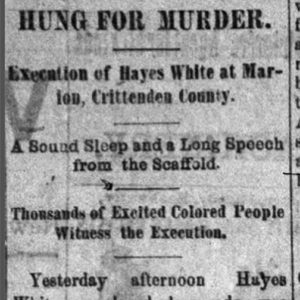 White Hayes (Execution of)
White Hayes (Execution of)
 Hernando de Soto Bridge
Hernando de Soto Bridge
 Highway 70 Bridge
Highway 70 Bridge
Hodges, Asa
 Asa Hodges
Asa Hodges
Hopefield (Crittenden County)
Hopefield, Burning of
 Horseshoe Lake
Horseshoe Lake
Horseshoe Lake (Crittenden County)
 Howlin' Wolf
Howlin' Wolf




