 George Dallas
George Dallas
Time Period: Louisiana Purchase through Early Statehood (1803 - 1860) - Starting with D
 George Dallas
George Dallas
Danley, Christopher Columbus
 David S. Lewis Execution Story
David S. Lewis Execution Story
Defender [Steamboat]
Dehahuit
 Der Squire
Der Squire
Der Squire: Ein Bild aus den Hinterwalden Nordamerikas
Dickinson, Thomas (Execution of)
Dickinson, Townsend
 Townsend Dickinson
Townsend Dickinson
Dover to Clarksville Road
Dowdy, John (Execution of)
 John Dowdy Execution Article
John Dowdy Execution Article
 John Drennen House
John Drennen House
Drennen-Scott Historic Site
 John Drennen
John Drennen
Drennen, John
 Thomas Drew
Thomas Drew
Drew, Thomas Stevenson
 Duel Story
Duel Story
 Duel Story
Duel Story
 Duwali
Duwali
Duwali
aka: Bowl
aka: Bowles
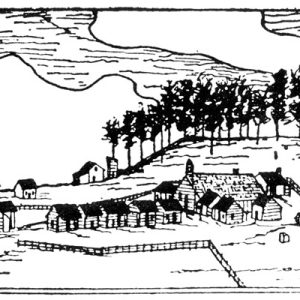 Dwight Mission
Dwight Mission




