Race and Ethnicity: African American - Starting with E
 Ebony Magazine
Ebony Magazine
 Eckford Bench
Eckford Bench
 Elizabeth Eckford
Elizabeth Eckford
 Elizabeth Eckford
Elizabeth Eckford
Eckford, Elizabeth Ann
 Ed Whitfield in High School
Ed Whitfield in High School
Eddie Mae Herron Center & Museum
aka: St. Mary’s AME Church (Pocahontas)
aka: Pocahontas Colored School
Edmondson Home and Improvement Company v. Harold E. Weaver
 El Dorado Race Riot Article
El Dorado Race Riot Article
El Dorado Race Riot of 1910
 Elaine Massacre Newspaper Article
Elaine Massacre Newspaper Article
 Elaine Massacre Defendants
Elaine Massacre Defendants
 Elaine Massacre Newspaper Article
Elaine Massacre Newspaper Article
 Elaine Massacre Defendants
Elaine Massacre Defendants
 Elaine Massacre Flyer
Elaine Massacre Flyer
Elaine Massacre of 1919
aka: Elaine Race Riot of 1919
aka: Elaine Race Massacre
 Elaine Massacre Prisoners
Elaine Massacre Prisoners
Elam, Lloyd Charles
 Lloyd Charles Elam
Lloyd Charles Elam
 Lloyd Charles Elam
Lloyd Charles Elam
 Lloyd Charles Elam
Lloyd Charles Elam
 Joycelyn Elders
Joycelyn Elders
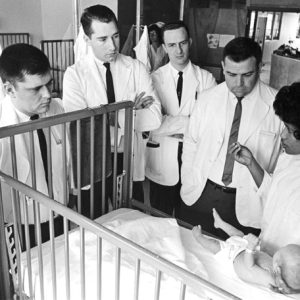 Joycelyn Elders
Joycelyn Elders
Elders, Joycelyn
aka: Minnie Lee Jones
Eleventh Regiment, United States Colored Troops (US)
Elligin and Anderson (Lynching of)
 Joyce Elliott
Joyce Elliott
 Ellison and Son
Ellison and Son
Ellison, Clyde (Lynching of)
Ellison, Eugene (Killing of)
Emancipation
 Embracing Wisdom II
Embracing Wisdom II
Ernest Green Story, The
 Ernie's Museum of Black Arkansas
Ernie's Museum of Black Arkansas
 Eugene Ellison
Eugene Ellison
Evans, David L.
 David Evans
David Evans
Evans, Grover
 Grover Evans
Grover Evans




