Entry Type: Thing - Starting with B
Bowfin
aka: Grinnell
 Bowfin
Bowfin
Bowie Knife
 Bowie Knife
Bowie Knife
 Bowie Knife
Bowie Knife
Boxcar Bertha
 Boxcar Bertha
Boxcar Bertha
Boy Erased
 Boy Erased
Boy Erased
 Boycott Flyer
Boycott Flyer
 Boyle Building
Boyle Building
 Boys Like Us by Peter McGehee
Boys Like Us by Peter McGehee
Boys on the Tracks, The
 Boys State Delegate
Boys State Delegate
Bozeman House
 William Claude Bradford Gravestone
William Claude Bradford Gravestone
Bradley County Courthouse and County Clerk’s Office
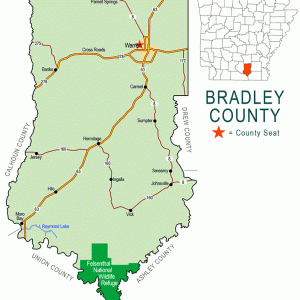 Bradley County Map
Bradley County Map
 Bradley Pink Tomato
Bradley Pink Tomato
Branchiobdellidans
aka: Crayfish Worms
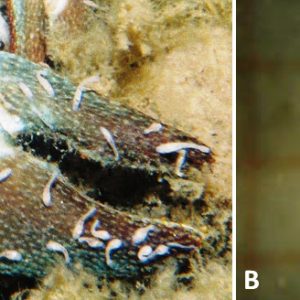 Branchiobdellids
Branchiobdellids
Brandon Burlsworth Foundation
 Doug Brandon Campaign Card
Doug Brandon Campaign Card
 Brandy Distillery
Brandy Distillery
Brandywine [Steamboat]
Brazeale Homestead
 Nicholas Brewer Landscape
Nicholas Brewer Landscape
Breweries
Brick Industry
 Bridge Street
Bridge Street
Bridge Street Bridge
 Bridge Street Bridge
Bridge Street Bridge
 Bridge Street Bridge Guard Rail
Bridge Street Bridge Guard Rail
 Bridge Street Bridge Support
Bridge Street Bridge Support
 Bridge Street Dedication Plaque
Bridge Street Dedication Plaque
Bridges
 "Bring Me to Life," Performed by Evanescence
"Bring Me to Life," Performed by Evanescence
Brinkley Argus
 Brinkley Hospital Brochure
Brinkley Hospital Brochure
 "Footsie" Britt Campaign Sticker
"Footsie" Britt Campaign Sticker
 Footsie Britt Tombstone
Footsie Britt Tombstone
 Broadhead Skinks
Broadhead Skinks
Broadway Bridge
 Broadway Bridge Demolition
Broadway Bridge Demolition
 Broadway Bridge Remodel
Broadway Bridge Remodel
 Broken Bow Lake
Broken Bow Lake
 Broken Promises by Greer Ferris
Broken Promises by Greer Ferris
Bromine
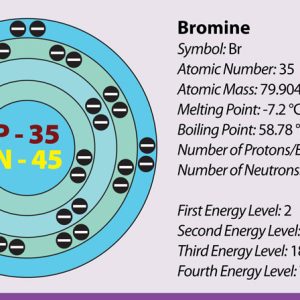 Bromine Atomic Information
Bromine Atomic Information




