Entry Type: Thing - Starting with P
 Pocahontas Bridge
Pocahontas Bridge
Pocahontas [Steamboat]
Pocahontas Post Office (Historic)
 Pocahontas Water Tank
Pocahontas Water Tank
 Pocket Gopher Mounds
Pocket Gopher Mounds
 Pocket Gopher Newborn
Pocket Gopher Newborn
Poesia
Poinsett County Courthouse
 Poinsett County Courthouse
Poinsett County Courthouse
 Poinsett County Map
Poinsett County Map
 Engagement at Poison Spring Marker
Engagement at Poison Spring Marker
 Poisonous Mushrooms
Poisonous Mushrooms
 Poisonous Mushrooms
Poisonous Mushrooms
Poisonous Mushrooms
 Poland Committee Article
Poland Committee Article
 Political Cartoon
Political Cartoon
Polk County Courthouse
 Polk County Map
Polk County Map
Poll Tax
 Poll Tax Receipt
Poll Tax Receipt
 Poll Tax Book
Poll Tax Book
 Polyphemus Moth
Polyphemus Moth
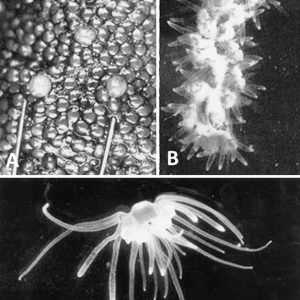 Polypodium hydriforme
Polypodium hydriforme
 Pondberry
Pondberry
Poorhouses
aka: Poor Farms
 Pope County Map
Pope County Map
 Popeye Statue
Popeye Statue
 Poppies and Eucalyptus
Poppies and Eucalyptus
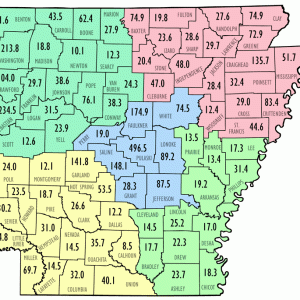 Population Density
Population Density
Populist Movement
aka: People's Party
aka: Populism
Porter Prize
aka: Porter Fund Literary Prize
 Possibly the USS Tensas
Possibly the USS Tensas
Post Familie Vineyards and Winery
 Post Familie Winery Bottle
Post Familie Winery Bottle
Post Office Art
Post-bellum Black Codes
aka: Black Codes
Poteau River
Poteau Work Center
 Poteau Work Center
Poteau Work Center
Pottery
Pottsville Citizens Bank
Poultry Industry
Poverty
 POW Stone
POW Stone
 Powder Magazine
Powder Magazine
 Dick Powell Home
Dick Powell Home
Powhatan Courthouse
Powhatan Jail
 Powhatan Jail Cell
Powhatan Jail Cell




