Entry Type: Thing - Starting with H
Historic Dyess Colony: Boyhood Home of Johnny Cash
aka: Johnny Cash Boyhood Home
Historic Preservation
Historical Archaeology
History of Hot Springs Gambling Museum
Hodges House
Hodges v. United States
 Hollandsworth Tombstone
Hollandsworth Tombstone
 Holt Landscape
Holt Landscape
 Holt Landscape
Holt Landscape
 Holt Landscape
Holt Landscape
 Holt Landscape
Holt Landscape
 Holt Seascape
Holt Seascape
 Holt Still Life
Holt Still Life
 George M. Holt Gravesite
George M. Holt Gravesite
 George M. Holt Marker
George M. Holt Marker
 Jack Wilson Holt Sr. Cartoon
Jack Wilson Holt Sr. Cartoon
Home Ice Company
 Home Ice Company
Home Ice Company
 Home Ice Company
Home Ice Company
Home News (McCrory)
Homelessness
Homer
 Homer Ad
Homer Ad
 Homer Steamboat Schedule
Homer Steamboat Schedule
Homestead Act of 1862
 Honey Comb
Honey Comb
 Honeybee, Official State Insect
Honeybee, Official State Insect
Hoo-Hoo Monument
 Hoo-Hoo Monument
Hoo-Hoo Monument
Hookworm Eradication
Hope Girl Scout Little House
 Hope Utilities
Hope Utilities
Horace Estes House
 Horace Estes House
Horace Estes House
 Horace Estes House
Horace Estes House
 Horace Mann High
Horace Mann High
Horace Mann School Historic District
 Horn Lookout Tower
Horn Lookout Tower
Hornibrook House
aka: Empress of Little Rock
 Horse Racing Marker
Horse Racing Marker
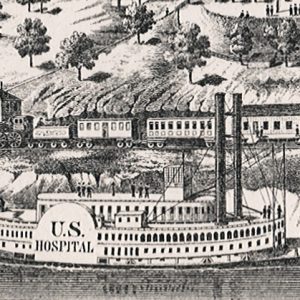 Hospital Steamer
Hospital Steamer
 Hospital Unit T Article
Hospital Unit T Article
 Hospital Unit T Paean
Hospital Unit T Paean
Hospitals (Civil War)
Hot Spring County Courthouse
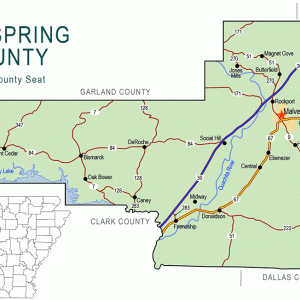 Hot Spring County Map
Hot Spring County Map
Hot Spring County Museum
aka: Boyle House
Hot Springs Confederate Monument
 Hot Springs Confederate Monument
Hot Springs Confederate Monument




