 Camp Magnolia COs
Camp Magnolia COs
Entry Type: Thing - Starting with C
 Camp Magnolia COs
Camp Magnolia COs
Camp Ozark
Campaign Finance Laws
 Campbell Children's Memorial
Campbell Children's Memorial
 Glen Campbell Sign
Glen Campbell Sign
 Canal
Canal
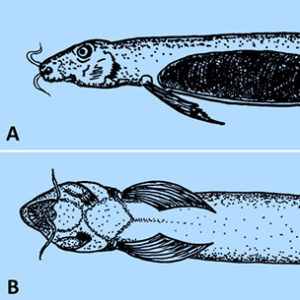 Candiru
Candiru
 Candle Stick Rock
Candle Stick Rock
 Cane Hill College
Cane Hill College
 Cane Hill Mill
Cane Hill Mill
 CAP Aircraft
CAP Aircraft
 Capital Citizens' Council Graphic
Capital Citizens' Council Graphic
 Capital Citizens' Council Anti-integration Flyer
Capital Citizens' Council Anti-integration Flyer
 Capital Citizens' Council Graphic
Capital Citizens' Council Graphic
 Capital Guards Memorial
Capital Guards Memorial
 Capital Guards Memorial Vandalism
Capital Guards Memorial Vandalism
 Capital Guards Monument Dedication
Capital Guards Monument Dedication
Capital Punishment
aka: Death Penalty
 Capitol Construction
Capitol Construction
Captain Charles C. Henderson House
aka: Henderson House
Captain Goodgame House
Captain Isaac N. Deadrick House
Captain John T. Burkett House
 Captured Still
Captured Still
Car of Commerce [Steamboat]
 "Car Wheels on a Gravel Road," Performed by Lucinda Williams
"Car Wheels on a Gravel Road," Performed by Lucinda Williams
Caraway Hall (Arkansas Tech University)
 Caraway Tribute
Caraway Tribute
 Hattie Caraway Stamp Program
Hattie Caraway Stamp Program
 Hattie Caraway Stamp
Hattie Caraway Stamp
 Hattie Caraway Appointment Certificate
Hattie Caraway Appointment Certificate
 Cardinal Plate
Cardinal Plate
 CAREN Equipment
CAREN Equipment
 CAREN Tower
CAREN Tower
Carlisle Independent
 Carlisle Rice Mill
Carlisle Rice Mill
 "Carmean Did It"
"Carmean Did It"
Carnegie Libraries
 Carolina Anemone
Carolina Anemone
 Carolina Larkspur
Carolina Larkspur
Carolina Methodist Church
Caroline [Steamboat]
 Caroline Steamboat Article
Caroline Steamboat Article
Carpenter Dam
aka: Lake Hamilton
 Carpenter Dam Construction
Carpenter Dam Construction
 Carpenter Dam Construction
Carpenter Dam Construction
 Carpet Rock
Carpet Rock
Carps
 Carps of Arkansas
Carps of Arkansas
 Carps of Arkansas
Carps of Arkansas




