 Little Portion Hermitage
Little Portion Hermitage
Entry Type: Place - Starting with L
 Little Portion Hermitage
Little Portion Hermitage
 Little Portion Hermitage
Little Portion Hermitage
 Little Red River
Little Red River
 Little Red River
Little Red River
 Little Red River Valley
Little Red River Valley
Little River (Northeastern Arkansas)
Little River County
 Little River County Courthouse
Little River County Courthouse
 Little River County Courthouse
Little River County Courthouse
Little Rock (Pulaski County)
 Little Rock City Hall
Little Rock City Hall
 Little Rock Stables
Little Rock Stables
 Little Rock; 1956
Little Rock; 1956
 Little Rock Fire Department
Little Rock Fire Department
 Little Rock Aerial View
Little Rock Aerial View
Little Rock Air Force Base
 Little Rock Air Force Base
Little Rock Air Force Base
 Little Rock and Fort Steele
Little Rock and Fort Steele
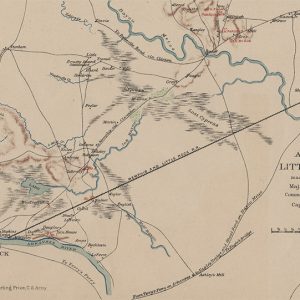 Little Rock Approaches
Little Rock Approaches
Little Rock Arsenal
Little Rock Aviation Supply Depot
 Little Rock Aviation Supply Depot
Little Rock Aviation Supply Depot
 Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
 Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
 Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
Little Rock Brewing & Ice Company
Little Rock Central High School National Historic Site
 Little Rock Central High Museum
Little Rock Central High Museum
Little Rock College
 Little Rock Downtown
Little Rock Downtown
 Little Rock Downtown Panorama
Little Rock Downtown Panorama
 Little Rock Fire Station No. 9
Little Rock Fire Station No. 9
 Little Rock Fire Station No. 9, Front View
Little Rock Fire Station No. 9, Front View
Little Rock Fortifications (Civil War)
 Little Rock Main Library
Little Rock Main Library
 Little Rock Main Street
Little Rock Main Street
Little Rock National Cemetery
 Little Rock National Cemetery
Little Rock National Cemetery
 Little Rock National Cemetery
Little Rock National Cemetery
 Little Rock Post Office
Little Rock Post Office
 Little Rock Public Library
Little Rock Public Library
 Little Rock Railway and Electric Co.
Little Rock Railway and Electric Co.
 Little Rock Skyline
Little Rock Skyline
 Little Rock Train Depot
Little Rock Train Depot
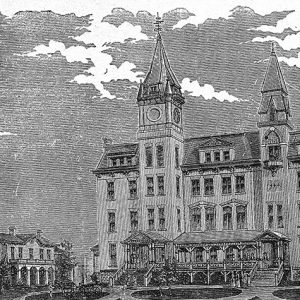 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
 Little Rock University
Little Rock University
Little Rock Zoo
 Little Rock Zoo
Little Rock Zoo
 Little Rock, 1933
Little Rock, 1933
 Little Rock, 1933
Little Rock, 1933




