Entry Type: Event - Starting with H
 Nat Hadley Lynching Article
Nat Hadley Lynching Article
Haguewood Prairie, Skirmish at
Hahn’s Farm, Skirmish at
aka: Skirmish at Waldron
Haley, Loy (Lynching of)
 Haley Lynching Article
Haley Lynching Article
Halfway House, Skirmish near the
Hall, Frank (Execution of)
 Hallie Steamboat Article
Hallie Steamboat Article
 Hamby Cholera Concern
Hamby Cholera Concern
Hamilton and Ludberry (Lynching of)
Hamilton, Henry (Reported Lynching of)
 Hampton Lynching Article
Hampton Lynching Article
Hampton Lynching of 1872
Hampton Race War of 1892
aka: Calhoun County Race War of 1892
 Hampton Race War Article
Hampton Race War Article
 Happy Hollow Tourists
Happy Hollow Tourists
Hardin, Will H. (Lynching of)
 Arthur Harding and J. Edgar Hoover
Arthur Harding and J. Edgar Hoover
Harper, John (Execution of)
 Harris Lynching
Harris Lynching
Harris, Frank (Lynching of)
 Frank Harris Lynching Article
Frank Harris Lynching Article
 Frank Harris Lynching Article
Frank Harris Lynching Article
 George Harris Lynching Article
George Harris Lynching Article
Harris, George (Lynching of)
Harris, Gilbert (Lynching of)
 Harris Lynching Article
Harris Lynching Article
Harris, Jack (Lynching of)
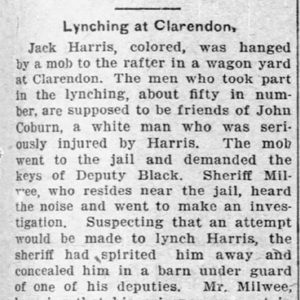 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Jack Harris Lynching Article
Jack Harris Lynching Article
 Harris Lynching Article
Harris Lynching Article
 Judge Harris Flees
Judge Harris Flees
 Harrison First Passenger Train
Harrison First Passenger Train
 Harrison Racial Expulsion Article
Harrison Racial Expulsion Article
Harrison Race Riots of 1905 and 1909
aka: Charles Stinnett (Execution of)
Harrison Railroad Riot
aka: Missouri and North Arkansas Railroad Strike
 Harrison Railroad Riot Article
Harrison Railroad Riot Article
Harrison, John Henry (Lawsuits Relating to the Lynching of)
Harrison, John Henry (Lynching of)
Harrison’s Landing, Skirmish at
Hatch’s Ferry, Skirmish at
Hay Station No. 3, Skirmish at
aka: Skirmish at Brownsville (July 30, 1864)
Hayden, Bud (Lynching of)
 Haden Lynching Article
Haden Lynching Article
Hearn, May (Lynching of)
 May Hearn Lynching Article
May Hearn Lynching Article
 Heifer Project International HQ Dedication
Heifer Project International HQ Dedication




