Entry Type: Event - Starting with D
aka: Bates v. City of Little Rock
 Dam Protesters
Dam Protesters
 Danville Lynching Article
Danville Lynching Article
Danville Lynching of 1883
Dardanelle and Ivey’s Ford, Actions at
 Dardanelle Flooding
Dardanelle Flooding
 Dardanelle Lynching Article
Dardanelle Lynching Article
Dardanelle Lynching of 1881
Dardanelle, Capture of
Dardanelle, Skirmish at (August 30, 1864)
Dardanelle, Skirmish at (September 12, 1863)
 Dave Ramsey Lynching Article
Dave Ramsey Lynching Article
 Odus Davidson at Gallows
Odus Davidson at Gallows
 Odus Davidson Trial
Odus Davidson Trial
 Chick Davis Lynching Article
Chick Davis Lynching Article
 Alford Davis Lynching Article
Alford Davis Lynching Article
Davis, Alford (Lynching of)
 Davis Lynching Article
Davis Lynching Article
Davis, Anthony (Lynching of)
Davis, Chick (Lynching of)
Davis, Elisha (Execution of)
 Herman Davis Funeral
Herman Davis Funeral
Davis, Howard (Lynching of)
 Howard Davis Lynching Article
Howard Davis Lynching Article
 Jeff Davis Campaign
Jeff Davis Campaign
Davis, Jim (Trial and Execution of)
 Jim Davis Article
Jim Davis Article
Davis, Lovett (Lynching of)
 Lovett Davis Lynching Article
Lovett Davis Lynching Article
Davis, Miller (Execution of)
De Soto Expedition, Route of the
 Arthur Dean Lynching Article
Arthur Dean Lynching Article
Dean, Arthur (Lynching of)
 Death Penalty Protest
Death Penalty Protest
Decatur Strike of 1951
 Defender Disaster Story
Defender Disaster Story
 Defender Disaster Story
Defender Disaster Story
Delta Symposium
Democratic Party Caucuses of 1984
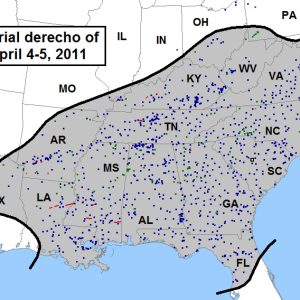 April 2011 Derecho / Area Affected
April 2011 Derecho / Area Affected
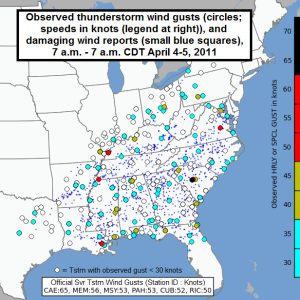 April, 2011 Derecho / Wind Gusts
April, 2011 Derecho / Wind Gusts
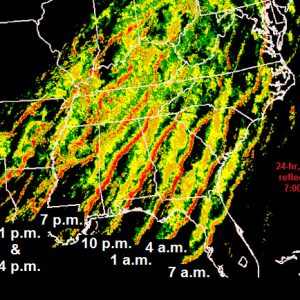 April 2011 Derecho
April 2011 Derecho
 Dermott 1927 Flood
Dermott 1927 Flood
 Dermott 1927 Flood
Dermott 1927 Flood
Dermott Crawfish Festival
 Dermott Crawfish Festival
Dermott Crawfish Festival




