Entry Category: Water - Starting with B
 Barge
Barge
Baring Cross Bridge
 Baring Cross Bridge
Baring Cross Bridge
Bart Tully [Steamboat]
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
 Bart Tully Article
Bart Tully Article
 Beaver Bridge
Beaver Bridge
 Before Norfork Lake
Before Norfork Lake
Belle Zane [Steamboat]
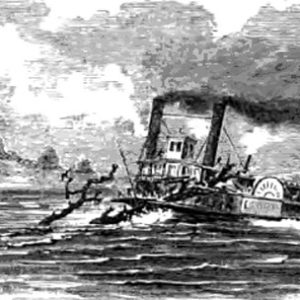 Belle Zane Steamboat
Belle Zane Steamboat
 Benton Bridge
Benton Bridge
Blakely Mountain Dam
aka: Blakely Dam
aka: Lake Ouachita
 Blakely Mountain Dam
Blakely Mountain Dam
 Blakely Mountain Dam
Blakely Mountain Dam
 Blansett Bridge
Blansett Bridge
Brandywine [Steamboat]
 Bridge 178
Bridge 178
Bridges
 Buffalo River Bridge
Buffalo River Bridge
Bull Shoals Dam and Lake
 Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants
Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants




