 Bobby Hopper Tunnel
Bobby Hopper Tunnel
Entry Category: Science and Medicine - Starting with B
 Bobby Hopper Tunnel
Bobby Hopper Tunnel
 Bobcat
Bobcat
Bodark
aka: Osage Orange
aka: Maclura pomifera
aka: Bois d'Arc
aka: Horse Apple
aka: Hedge Apple
 Bogus Cure
Bogus Cure
 Bois D'Arc Tree
Bois D'Arc Tree
 Bois D'Arc Tree
Bois D'Arc Tree
 Bois D'Arc Tree
Bois D'Arc Tree
 Boozman Campaign
Boozman Campaign
 Boozman Speaking
Boozman Speaking
Boozman, Fay
 Fay Boozman
Fay Boozman
Botanical Garden of the Ozarks
 Botanical Garden of the Ozarks
Botanical Garden of the Ozarks
 Botflies
Botflies
Bowfin
aka: Grinnell
Bowman, Malcolm Cleaburne
 Bowstring Bridge
Bowstring Bridge
 Boxley Elk
Boxley Elk
Branchiobdellidans
aka: Crayfish Worms
Branner, John Casper
Breland, Keller Bramwell
 Augustus L. Breysacher
Augustus L. Breysacher
Breysacher, Augustus Louis
Bridges
Brinkley, John Richard
 Broadhead Skinks
Broadhead Skinks
Broadway Bridge
 Broadway Bridge
Broadway Bridge
 Broadway Bridge Demolition
Broadway Bridge Demolition
 Broadway Bridge Remodel
Broadway Bridge Remodel
Bromine
Brooks, Ida Josephine
 Minnijean Brown
Minnijean Brown
Brownlee, Robert
 Rolfe Bryant
Rolfe Bryant
Bryozoans
aka: Ectoprocta
aka: Moss Animals
 Herbert Buchanan and George A. Campbell
Herbert Buchanan and George A. Campbell
 Herbert Buchanan
Herbert Buchanan
Buchanan, Herbert Earle
 Buffalo River Bridge
Buffalo River Bridge
 Building Demolition
Building Demolition
 Bull Shoals Dam
Bull Shoals Dam
Bull Shoals Dam and Lake
 Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants
Bull Shoals Dam Power Plants
 Bullhead Catfishes of Arkansas
Bullhead Catfishes of Arkansas
 Bumpers Vaccine Research Center
Bumpers Vaccine Research Center
 Ruth Burks
Ruth Burks
 Burying Beetles
Burying Beetles
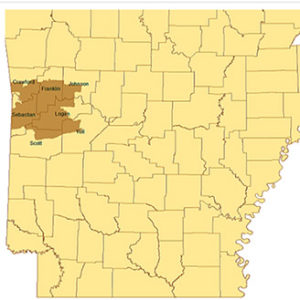 Burying Beetles Distribution
Burying Beetles Distribution
 Busey Oil Ad
Busey Oil Ad




