Entry Category: Race - Starting with M
 Lee Morrison Lynching Article
Lee Morrison Lynching Article
 William Morrison Lynching Article
William Morrison Lynching Article
 William Morrison Lynching Article
William Morrison Lynching Article
 Mosaic Templars Headquarters
Mosaic Templars Headquarters
Mosaic Templars of America
 Mosaic Templars of America Seal
Mosaic Templars of America Seal
Mosely, Julius (Lynching of)
Mothers’ League of Central High School
 Mothershed Marker
Mothershed Marker
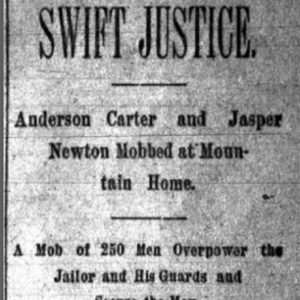 Mountain Home Lynching Article
Mountain Home Lynching Article
Mullens, Nat (Lynching of)
 Nat Mullens Lynching Article
Nat Mullens Lynching Article
 Murfreesboro Colored School
Murfreesboro Colored School




