 Calico Rock Music Hall
Calico Rock Music Hall
Entry Category: Institutions and Buildings - Starting with C
 Calico Rock Music Hall
Calico Rock Music Hall
 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Sanctuary
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Sanctuary
 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church
 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Construction
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Construction
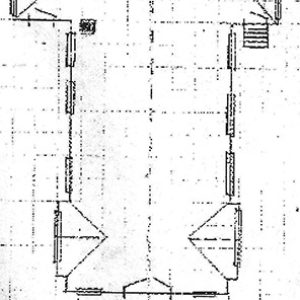 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Architectural Drawing
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Architectural Drawing
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church
aka: Calico Rock Music Hall
 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Ceiling
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church Ceiling
 Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church
Calico Rock Methodist Episcopal Church
 Camden Baptist Church
Camden Baptist Church
 Camden Church
Camden Church
 Camden Church
Camden Church
 Camden Church
Camden Church
Camp Aldersgate
 Camp Aldersgate
Camp Aldersgate
 Camp Aldersgate Campers
Camp Aldersgate Campers
 Camp Aldersgate Dance
Camp Aldersgate Dance
 Camp Aldersgate Entrance
Camp Aldersgate Entrance
 Camp Aldersgate Office
Camp Aldersgate Office
 Camp Aldersgate Swimming
Camp Aldersgate Swimming
 Camp Aldersgate Tree House
Camp Aldersgate Tree House
 Camp Aldersgate Waterfall
Camp Aldersgate Waterfall
Camp Magnolia
 Camp Magnolia
Camp Magnolia
 Camp Magnolia COs
Camp Magnolia COs
 Camp Magnolia Workers
Camp Magnolia Workers
Camp Ozark
 Camp Springs Methodist Church after Tornado Damage
Camp Springs Methodist Church after Tornado Damage
 Caney Church
Caney Church
 Carlisle Church
Carlisle Church
Carmelite Monastery of St. Teresa of Jesus
Carolina Methodist Church
 Carolina Methodist Church
Carolina Methodist Church
Cathedral of St. Andrew
aka: St. Andrew's Catholic Cathedral
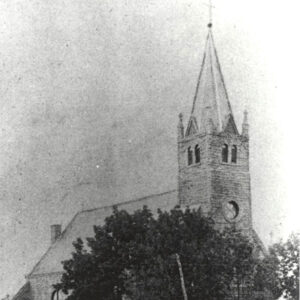 Catholic Church
Catholic Church
 Catholic High School for Boys
Catholic High School for Boys
Catholic High School for Boys (CHS)
aka: Little Rock Catholic High School for Boys
 Cato Church Bathrooms
Cato Church Bathrooms
 Cato Church Pews
Cato Church Pews
 Cedar Creek Community Church
Cedar Creek Community Church
 Cedar Creek Baptist Church
Cedar Creek Baptist Church
 Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
 Centennial Baptist Church
Centennial Baptist Church
Central Baptist College
 Central College Students
Central College Students
 Charleston Church
Charleston Church
 Christ Church Crucifier
Christ Church Crucifier
Christ Church Parochial and Industrial School
 Christ Church Parochial and Industrial School
Christ Church Parochial and Industrial School
 Christ Church Parochial School Buildings
Christ Church Parochial School Buildings




